Alkaline Peptone Water (pH 8.6)
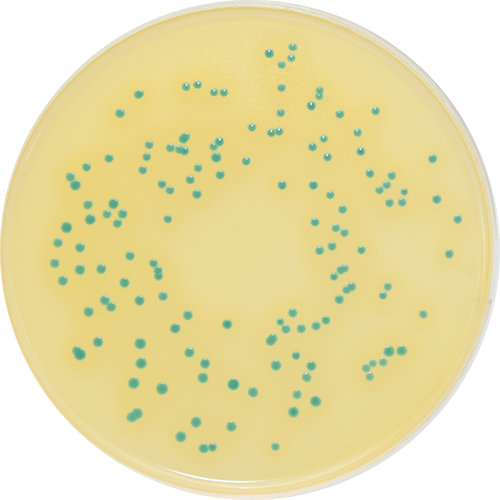
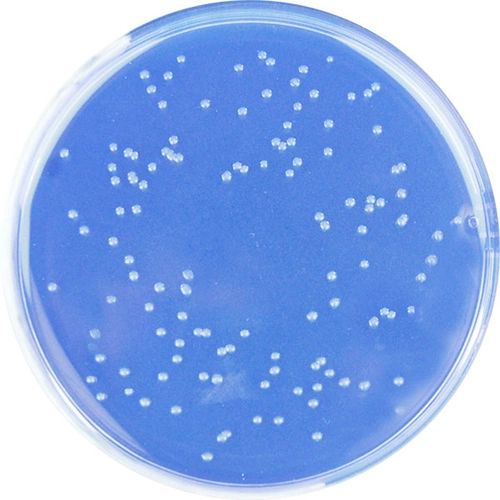
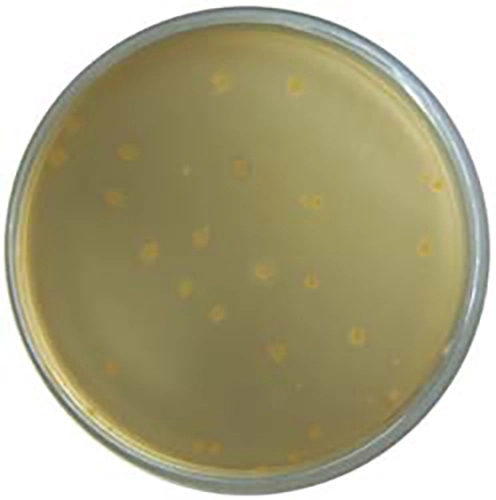
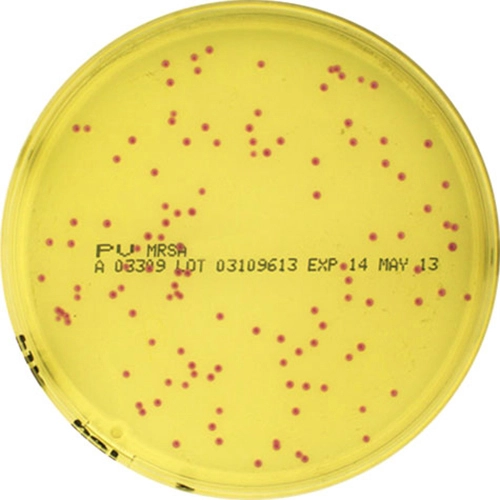
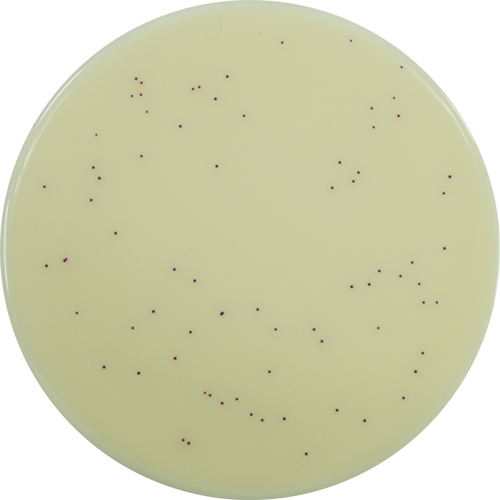
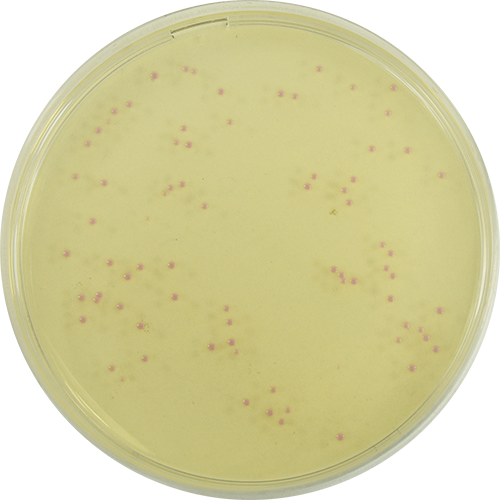
Colorex™ MRSA is a chromogenic medium for the selective isolation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The medium can be used for the routine screening of clinical specimens for MRSA from a variety of sampling sites such as the nose, throat and groin. The medium incorporates a nutritious peptone base medium and a number of selective agents to inhibit most Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria as well as yeasts and moulds. The chromogenic detection of specific enzyme activity leads to the formation of pink/mauve colonies indicating MRSA (including low level resistant and hetero-resistant strains) following incubation at 37°C for 18-24 hours. Other organisms, if present are indicated by blue or colourless colonies. Any presumptive isolates must be confirmed using serological and/or biochemical techniques available to the laboratory. The use of this chromogenic medium does not diminish the requirement for conventional antimicrobial susceptibility tests for the confirmation of methicillin resistance.
Limitations:
1. S.aureus strains that possess a low MIC to the selective agent present in the medium but are mec A negative may form colonies on the medium.
2. Some MRSA strains may form typical colonies surrounded by a matte halo. The formation of the halo serves no diagnostic function.
3. Certain methicillin-resistant coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) may produce characteristic colonies. In some cases differentiation may be achieved by examination of the colour of these colonies, as they may be considerably darker in colour (bluish purple to a very dark pink/magenta).
4. Certain bacterial species other than staphylococci may produce colonies with a characteristic colour.